- 取得連結
- X
- 以電子郵件傳送
- 其他應用程式
電路知識:Buck Converter
簡介:Buck Converter 原理
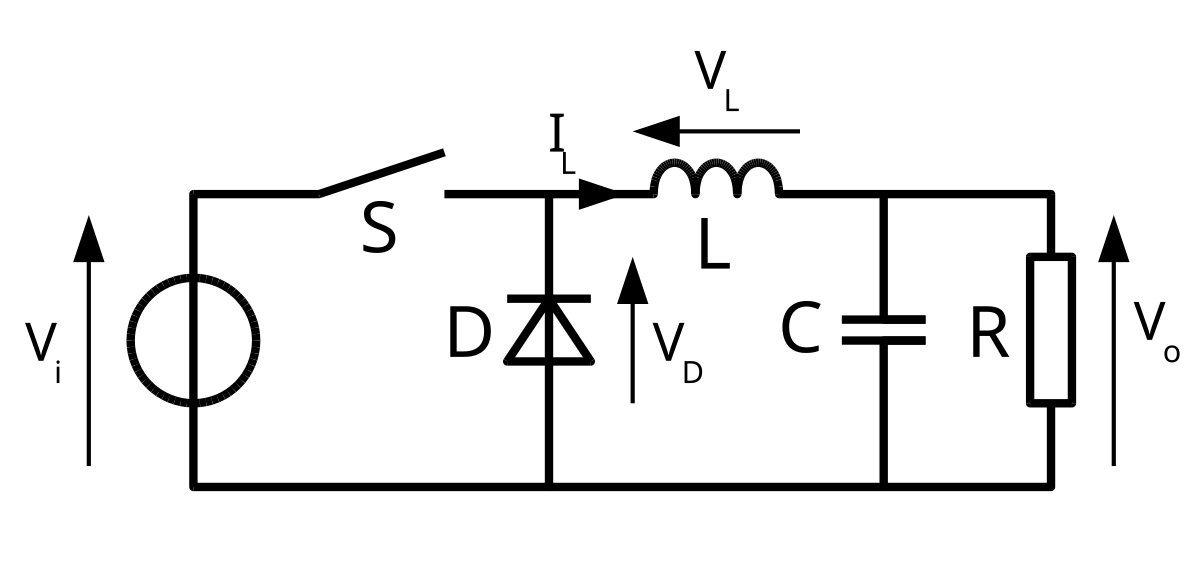 CyrilB~commonswiki assumed (based on copyright claims). - No machine-readable source provided. Own work assumed (based on copyright claims)., CC BY-SA 3.0, Link
CyrilB~commonswiki assumed (based on copyright claims). - No machine-readable source provided. Own work assumed (based on copyright claims)., CC BY-SA 3.0, Link
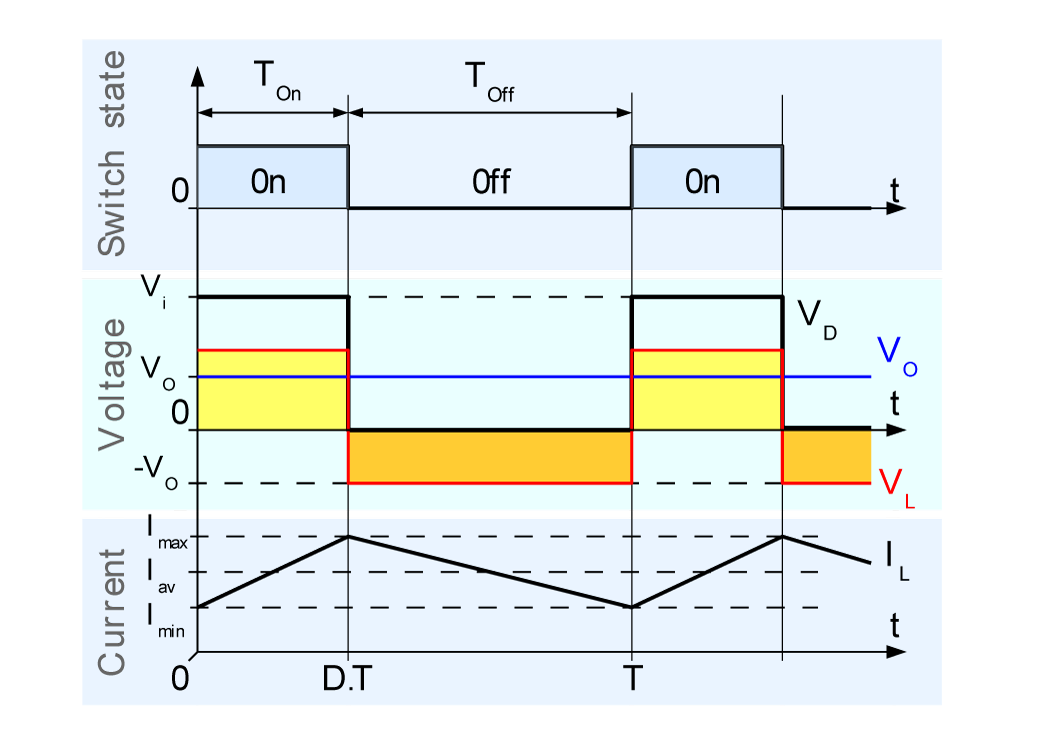
By Buck_chronogram.svg: efadae derivative work: Efadae (talk) - Buck_chronogram.svg, CC BY-SA 3.0, Link
$$ \begin{cases} V_o=V_i-V_{sw}-V_L & \text{ if } t\ in\ T_{on}=DT \\ V_o=-V_L+V_D & \text{ if } t\ in\ T_{off}=(1-D)T \\ \end{cases}\\ $$ 平均輸出電壓 $$ \begin{align*} V_{o,av}&=\frac{1}{T}\int_{0}^{t}V_o(t)\mathrm{d} t \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_o(t)\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_o(t)\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}(V_i-V_{sw}-V_L)\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}}^{T}(-V_L+V_D)\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_i\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_L\mathrm{d} t - \int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_L\mathrm{d} t+\int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_D\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_i\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T}V_L\mathrm{d} t +\int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_D\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (DTV_i-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t-0 +\int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_D\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= DV_i-\frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t -\int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_D\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ \end{align*} $$ $$ V_L=L\frac{\mathrm{d}I_L }{\mathrm{d} t} \\ $$ $$ \begin{align*} \Delta I_{L_{on}}&=I_{max}-I_{min} \\ &= \int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_L}{L} \mathrm{d} t \\ &= \int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_i-V_{sw}-V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ &= \int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_i}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ &= \frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \\\\ \Delta I_{L_{off}}&=I_{min}-I_{max} \\ &= \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_L}{L} \mathrm{d} t \\ &= \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{-V_o+V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{align*} $$ $$ \begin{align*} \Delta I_{L_{on}}=I_{max}-I_{min} &= \frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \Delta I_{L_{off}}=I_{min}-I_{max} &= \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{-V_o+V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{align*} $$ 從另一方面解 \(V_{o,av}\),因電感電流穩定
$$ \begin{align*} 0 &= \Delta I_{L_{on}} + \Delta I_{L_{off}} \\ 0 &= \frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{-V_o+V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t\\ 0 &= \frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t\\ \int_{0}^{T}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t &= \frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t\\ \int_{0}^{T}V_o\mathrm{d} t &= DTV_i-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_D\mathrm{d} t\\ \frac{1}{T}\int_{0}^{T}V_o\mathrm{d} t &= DV_i-\frac{1}{T}\int_{0}^{T_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t + \frac{1}{T}\int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_D\mathrm{d} t\\ V_{o,av} &= DV_i-\frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{T_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t -\int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_D\mathrm{d} t \right )\\ \end{align*} $$ 因電感平均電流位於最大值與最小值的中間
又根據之前推導的 \(\Delta I_{L_{on}}\) 可得下面兩式
$$ \left\{\begin{matrix} I_{max}+I_{min}&=&2*I_{av}\\ I_{max}-I_{min} &=& \frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{matrix}\right.\\ \left\{\begin{matrix} 2 \cdot I_{max} &=&2*I_{av} + \frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t\\ 2 \cdot I_{min} &=&2*I_{av} - \frac{DTV_i}{L}+\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t+\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{matrix}\right.\\ \left\{\begin{matrix} I_{max} &=&I_{av} + \frac{DTV_i}{2L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{2L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{2L}\mathrm{d} t\\ I_{min} &=&I_{av} - \frac{DTV_i}{2L}+\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{2L}\mathrm{d} t+\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{2L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{matrix}\right.\\ $$ 或者根據之前推導的 \(\Delta I_{L_{off}}\) 可得下面兩式
$$ \left\{\begin{matrix} I_{max}+I_{min} &=&2*I_{av}\\ I_{min}-I_{max} &=& \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{-V_o+V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{matrix}\right.\\ \left\{\begin{matrix} I_{max}+I_{min} &=&2*I_{av}\\ I_{max}-I_{min} &=& \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{matrix}\right.\\ \left\{\begin{matrix} 2 \cdot I_{max} &=&2*I_{av} + \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t\\ 2 \cdot I_{min} &=&2*I_{av} - \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{matrix}\right.\\ \left\{\begin{matrix} I_{max} &=&I_{av} + \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{2L}\mathrm{d} t\\ I_{min} &=&I_{av} - \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{2L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{matrix}\right.\\ $$ 保持 continuous mode 的條件,就是 \(I_L \geq 0\)
$$ \begin{align*} I_{min} &=I_{av} - \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{2L}\mathrm{d} t \geq 0\\ I_{av} & \geq \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{2L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \frac{V_{o,av}}{R} & \geq \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{2L}\mathrm{d} t \\ L & \geq \frac{R}{2V_{o,av}}\int_{t_{on}}^{T}(V_o-V_D)\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{align*} $$ 前提假設,電容很大,所以負載 \(R\) 的電流趨近於直流
故 \(I_{av}\) 為 \(R\) 的電流
$$ \begin{align*} Q&=CV_C\\ I_C&=C\frac{\mathrm{d} V_C}{\mathrm{d} t}\\ I_L &= I_C + I_R \\ I_{av} + \Delta I_L &= C\frac{\mathrm{d} V_C}{\mathrm{d} t} + I_{av}\\ \Delta I_L &= C\frac{\mathrm{d} V_C}{\mathrm{d} t}\\ \int_{t_1}^{t_2}\frac{\Delta I_L}{C}\mathrm{d} t &=\Delta V_C \end{align*} $$ 取 \(I_L > I_{av}\) 的 \(\Delta I_L\) 可得最大 Voltage Ripple
直接求三角形面積
$$ \begin{align*} \Delta V_C &=\int_{t_1}^{t_2}\frac{\Delta I_L}{C}\mathrm{d} t\\ &=\frac{1}{C} \cdot \frac{1}{2}\cdot \frac{\Delta I_L}{2}\cdot \frac{T}{2}\\ &=\frac{\Delta I_L T}{8C} \end{align*} $$

By No machine-readable author provided. CyrilB~commonswiki assumed (based on copyright claims). - No machine-readable source provided. Own work assumed (based on copyright claims)., CC BY-SA 3.0, Link $$ \begin{cases} V_o=V_i-V_{sw}-V_L & \text{ if } t\ in\ T_{on}=DT \\ V_o=-V_L+V_D& \text{ if } t\ in\ \delta T \\ V_o=V_C & \text{ if } t\ in\ others \\ \end{cases}\\ $$ 平均輸出電壓 $$ \begin{align*} V_{o,av}&=\frac{1}{T}\int_{0}^{t}V_o(t)\mathrm{d} t \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_o(t)\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_o(t)\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}+\delta T}^{T}V_o(t)\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}(V_i-V_{sw}-V_L)\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}(-V_L+V_D)\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}+\delta T}^{T}V_C\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_i\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_L\mathrm{d} t - \int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_L\mathrm{d} t+\int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_D\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}+\delta T}^{T}V_C\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_i\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_L\mathrm{d} t +\int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_D\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}+\delta T}^{T}V_C\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (DTV_i-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t-0 +\int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_D\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}+\delta T}^{T}V_C\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (DTV_i-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t +\int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_D\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}+\delta T}^{T}V_C\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= DV_i - \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t -\int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_D\mathrm{d} t - \int_{t_{on}-\delta T}^{T}V_C\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ \end{align*} $$ $$ V_L=L\frac{\mathrm{d}I_L }{\mathrm{d} t} \\ $$ $$ \begin{align*} \Delta I_{L_{on}}&=I_{max}-I_{min} \\ &= \int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_L}{L} \mathrm{d} t \\ &= \int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_i-V_{sw}-V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ &= \int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_i}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ &= \frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \\\\ \Delta I_{L_{off}}&=I_{min}-I_{max} \\ &= \int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}\frac{V_L}{L} \mathrm{d} t \\ &= \int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}\frac{-V_o+V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{align*} $$
Inductor Calculation for Buck Converter IC
STUDY AND DESIGN OF BUCK CONVERTER
- Tool:
- Qucs
簡介:Buck Converter 原理
 CyrilB~commonswiki assumed (based on copyright claims). - No machine-readable source provided. Own work assumed (based on copyright claims)., CC BY-SA 3.0, Link
CyrilB~commonswiki assumed (based on copyright claims). - No machine-readable source provided. Own work assumed (based on copyright claims)., CC BY-SA 3.0, Link設計概念
Continuous mode
$$ \begin{align*} V_{o,av}&=DV_i-\frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t -\int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_D\mathrm{d} t \right )\\ \Delta I_L&=\frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t=\int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t\\ I_{av} &= \frac{V_{o,av}}{R}\\ L &\geq \frac{R}{2V_{o,av}}\int_{t_{on}}^{T}(V_o-V_D)\mathrm{d} t \\ V_{ripple} &= \frac{\Delta I_LT}{8C}\ if\ C\ is\ large\\ \end{align*} $$
By Buck_chronogram.svg: efadae derivative work: Efadae (talk) - Buck_chronogram.svg, CC BY-SA 3.0, Link
$$ \begin{cases} V_o=V_i-V_{sw}-V_L & \text{ if } t\ in\ T_{on}=DT \\ V_o=-V_L+V_D & \text{ if } t\ in\ T_{off}=(1-D)T \\ \end{cases}\\ $$ 平均輸出電壓 $$ \begin{align*} V_{o,av}&=\frac{1}{T}\int_{0}^{t}V_o(t)\mathrm{d} t \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_o(t)\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_o(t)\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}(V_i-V_{sw}-V_L)\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}}^{T}(-V_L+V_D)\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_i\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_L\mathrm{d} t - \int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_L\mathrm{d} t+\int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_D\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_i\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T}V_L\mathrm{d} t +\int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_D\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (DTV_i-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t-0 +\int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_D\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= DV_i-\frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t -\int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_D\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ \end{align*} $$ $$ V_L=L\frac{\mathrm{d}I_L }{\mathrm{d} t} \\ $$ $$ \begin{align*} \Delta I_{L_{on}}&=I_{max}-I_{min} \\ &= \int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_L}{L} \mathrm{d} t \\ &= \int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_i-V_{sw}-V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ &= \int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_i}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ &= \frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \\\\ \Delta I_{L_{off}}&=I_{min}-I_{max} \\ &= \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_L}{L} \mathrm{d} t \\ &= \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{-V_o+V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{align*} $$ $$ \begin{align*} \Delta I_{L_{on}}=I_{max}-I_{min} &= \frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \Delta I_{L_{off}}=I_{min}-I_{max} &= \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{-V_o+V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{align*} $$ 從另一方面解 \(V_{o,av}\),因電感電流穩定
$$ \begin{align*} 0 &= \Delta I_{L_{on}} + \Delta I_{L_{off}} \\ 0 &= \frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{-V_o+V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t\\ 0 &= \frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t\\ \int_{0}^{T}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t &= \frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t\\ \int_{0}^{T}V_o\mathrm{d} t &= DTV_i-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_D\mathrm{d} t\\ \frac{1}{T}\int_{0}^{T}V_o\mathrm{d} t &= DV_i-\frac{1}{T}\int_{0}^{T_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t + \frac{1}{T}\int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_D\mathrm{d} t\\ V_{o,av} &= DV_i-\frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{T_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t -\int_{t_{on}}^{T}V_D\mathrm{d} t \right )\\ \end{align*} $$ 因電感平均電流位於最大值與最小值的中間
又根據之前推導的 \(\Delta I_{L_{on}}\) 可得下面兩式
$$ \left\{\begin{matrix} I_{max}+I_{min}&=&2*I_{av}\\ I_{max}-I_{min} &=& \frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{matrix}\right.\\ \left\{\begin{matrix} 2 \cdot I_{max} &=&2*I_{av} + \frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t\\ 2 \cdot I_{min} &=&2*I_{av} - \frac{DTV_i}{L}+\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t+\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{matrix}\right.\\ \left\{\begin{matrix} I_{max} &=&I_{av} + \frac{DTV_i}{2L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{2L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{2L}\mathrm{d} t\\ I_{min} &=&I_{av} - \frac{DTV_i}{2L}+\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{2L}\mathrm{d} t+\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{2L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{matrix}\right.\\ $$ 或者根據之前推導的 \(\Delta I_{L_{off}}\) 可得下面兩式
$$ \left\{\begin{matrix} I_{max}+I_{min} &=&2*I_{av}\\ I_{min}-I_{max} &=& \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{-V_o+V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{matrix}\right.\\ \left\{\begin{matrix} I_{max}+I_{min} &=&2*I_{av}\\ I_{max}-I_{min} &=& \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{matrix}\right.\\ \left\{\begin{matrix} 2 \cdot I_{max} &=&2*I_{av} + \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t\\ 2 \cdot I_{min} &=&2*I_{av} - \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{matrix}\right.\\ \left\{\begin{matrix} I_{max} &=&I_{av} + \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{2L}\mathrm{d} t\\ I_{min} &=&I_{av} - \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{2L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{matrix}\right.\\ $$ 保持 continuous mode 的條件,就是 \(I_L \geq 0\)
$$ \begin{align*} I_{min} &=I_{av} - \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{2L}\mathrm{d} t \geq 0\\ I_{av} & \geq \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{2L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \frac{V_{o,av}}{R} & \geq \int_{t_{on}}^{T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{2L}\mathrm{d} t \\ L & \geq \frac{R}{2V_{o,av}}\int_{t_{on}}^{T}(V_o-V_D)\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{align*} $$ 前提假設,電容很大,所以負載 \(R\) 的電流趨近於直流
故 \(I_{av}\) 為 \(R\) 的電流
$$ \begin{align*} Q&=CV_C\\ I_C&=C\frac{\mathrm{d} V_C}{\mathrm{d} t}\\ I_L &= I_C + I_R \\ I_{av} + \Delta I_L &= C\frac{\mathrm{d} V_C}{\mathrm{d} t} + I_{av}\\ \Delta I_L &= C\frac{\mathrm{d} V_C}{\mathrm{d} t}\\ \int_{t_1}^{t_2}\frac{\Delta I_L}{C}\mathrm{d} t &=\Delta V_C \end{align*} $$ 取 \(I_L > I_{av}\) 的 \(\Delta I_L\) 可得最大 Voltage Ripple
直接求三角形面積
$$ \begin{align*} \Delta V_C &=\int_{t_1}^{t_2}\frac{\Delta I_L}{C}\mathrm{d} t\\ &=\frac{1}{C} \cdot \frac{1}{2}\cdot \frac{\Delta I_L}{2}\cdot \frac{T}{2}\\ &=\frac{\Delta I_L T}{8C} \end{align*} $$
Discontinuous mode
$$ \begin{align*} V_{o,av} &=DV_i - \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t -\int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_D\mathrm{d} t - \int_{t_{on}-\delta T}^{T}V_C\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ \Delta I_L&=\frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t=\int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}\frac{V_o-V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t\\ \end{align*} $$
By No machine-readable author provided. CyrilB~commonswiki assumed (based on copyright claims). - No machine-readable source provided. Own work assumed (based on copyright claims)., CC BY-SA 3.0, Link $$ \begin{cases} V_o=V_i-V_{sw}-V_L & \text{ if } t\ in\ T_{on}=DT \\ V_o=-V_L+V_D& \text{ if } t\ in\ \delta T \\ V_o=V_C & \text{ if } t\ in\ others \\ \end{cases}\\ $$ 平均輸出電壓 $$ \begin{align*} V_{o,av}&=\frac{1}{T}\int_{0}^{t}V_o(t)\mathrm{d} t \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_o(t)\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_o(t)\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}+\delta T}^{T}V_o(t)\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}(V_i-V_{sw}-V_L)\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}(-V_L+V_D)\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}+\delta T}^{T}V_C\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_i\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_L\mathrm{d} t - \int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_L\mathrm{d} t+\int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_D\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}+\delta T}^{T}V_C\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_i\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_L\mathrm{d} t +\int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_D\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}+\delta T}^{T}V_C\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (DTV_i-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t-0 +\int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_D\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}+\delta T}^{T}V_C\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= \frac{1}{T}\left (DTV_i-\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t +\int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_D\mathrm{d} t + \int_{t_{on}+\delta T}^{T}V_C\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ &= DV_i - \frac{1}{T}\left (\int_{0}^{t_{on}}V_{sw}\mathrm{d} t -\int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}V_D\mathrm{d} t - \int_{t_{on}-\delta T}^{T}V_C\mathrm{d} t \right ) \\ \end{align*} $$ $$ V_L=L\frac{\mathrm{d}I_L }{\mathrm{d} t} \\ $$ $$ \begin{align*} \Delta I_{L_{on}}&=I_{max}-I_{min} \\ &= \int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_L}{L} \mathrm{d} t \\ &= \int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_i-V_{sw}-V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ &= \int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_i}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ &= \frac{DTV_i}{L}-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_{sw}}{L}\mathrm{d} t-\int_{0}^{T_{on}}\frac{V_o}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \\\\ \Delta I_{L_{off}}&=I_{min}-I_{max} \\ &= \int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}\frac{V_L}{L} \mathrm{d} t \\ &= \int_{t_{on}}^{t_{on}+\delta T}\frac{-V_o+V_D}{L}\mathrm{d} t \\ \end{align*} $$
Simulation GitHub
參考
Buck converterInductor Calculation for Buck Converter IC
STUDY AND DESIGN OF BUCK CONVERTER


留言
張貼留言